These ‘articles in a nutshell’ provide a balanced, straightforward and realistic overview of new science in Parkinson’s, and what it really means in the context of moving towards a cure.
COVID-19
It will take months or possibly years to definitively appreciate how the COVID-19 pandemic will affect people with
Focus on LRRK2 inhibition – implications for idiopathic Parkinson’s
A new preclinical study has shown that LRRK2 inhibition in an animal model of Parkinson’s can improve lysosomal health and reduce alpha synuclein accumulation in dopaminergic neurons.
Gut infection triggers Parkinson’s-like symptoms in mice
PINK1 may also protect cells and the brain from autoimmune attack
Discovering genetics of age at onset
Using the largest ever genetics dataset
Parkinson Matters: A Call to Action
Discrepancies between end of life preferences
Global Parkinson’s Pandemic
Parkinson’s is now held to be the fastest growing neurological disorder.
Changes in gut and Parkinson’s risk
Recent studies show a link between the gut and Parkinson’s.
Gene linked to inherited Parkinson’s identified
TMEM230 gene association with familial cases of Parkinson’s.
Wide-reaching implications of recent research into GBA
New research into the cellular clearance pathways governed by the GBA gene has shown reduced activity associated with both ageing and idiopathic Parkinson’s.
Genetic findings from the Tracking PD study
Largest UK population based study of PD found up to 10% of affected individuals carry a pathogenic mutation
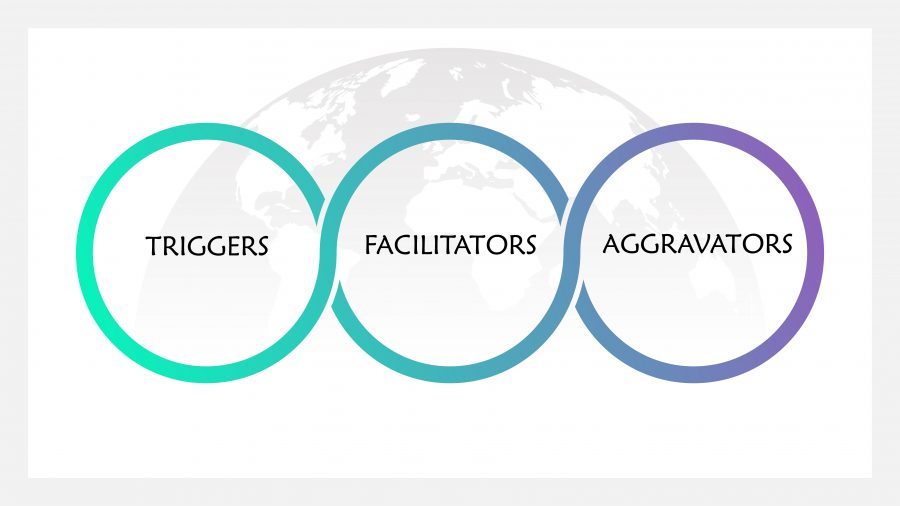
Triggers, Facilitators and Aggravators
New hypothesis which could reconceptualise Parkinson’s
LRRK2 and inflammation
Disease modifying efforts focusing on LRRK2
Salbutamol and Parkinson’s
Common asthma drug may reduce Parkinson’s risk
PD incidence increases over 30 years
Environmental factors could be connected to increase in Parkinson’s.
Falls and fractures precede Parkinson’s diagnosis
Falls and hip fractures may be indicative of Parkinson’s later in life.
LRRK2 and GBA: A window of opportunity for early intervention?
Analysis of the PPMI dataset has shown that compared to people with sporadic forms of Parkinson’s, newly diagnosed people carrying GBA mutations are less severely impaired, and those with LRRK2 mutations appear more mildly affected.
Early changes in GBA1 carriers without PD
Changes in smell, mood, and cognition in people with GBA1 mutations
Mediterranean diet and early symptoms
Mediterranean diet seen to lower symptom risk
LRRK2 gene in Crohn’s and Parkinson’s
Study has found shared variants of LRRK2 gene.
Hepatitis B & C linked to risk of Parkinson’s
Increased association found between hepatitis B and C and Parkinson’s.
Study uncovers role of PD-related gene
Scientists uncovered how LRRK2 gene regulates cellular transport.
Pesticides linked to increase in PD risk
Pesticides inhibiting ALDH enzyme and increased Parkinson’s disease risk.